Rosemary Oil for Hair: What Do We Know About Its Effectiveness?
Rosemary oil has gained recognition as a natural remedy for hair loss, with studies showing results comparable to minoxidil in some cases. While it may improve scalp health and hair density, natural treatments often fall short for hair loss.
Post Author:
medicalhair
Categories:
Date Posted:
September 10, 2025
Share This:
Origins of Rosemary Oil
Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) is a term from the Lamiaceae family, which encompasses a variety of aromatic plants. While R. officinalis is the most widely recognized species, the genus Rosmarinus includes several other lesser known varieties.
Rosemary has long been used in traditional and folk medicine; modern scientific research has validated many of its therapeutic properties. Studies have demonstrated that rosemary exhibits significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, among other potential health benefits that support its role in contemporary medical and wellness practices.

Effectiveness of Rosemary Oil in Hair Loss
Recently, rosemary oil has seen a surge in popularity as a potential natural remedy for various health concerns. Although some of its traditional uses stem from folk medicine, modern research has increasingly validated its therapeutic properties. Scientific studies have identified key bioactive compounds in rosemary that exhibit notable anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may support the body’s healing processes.
In a randomized comparative trial published in 2015, researchers evaluated the effectiveness of rosemary oil versus 2% minoxidil in individuals with androgenetic alopecia. Notably, the group treated with rosemary oil showed comparable improvements to those using minoxidil, suggesting that rosemary oil may serve as an effective natural alternative for individuals seeking hair regrowth without the potential side effects associated with pharmaceutical options.
How to Use
Scalp Massage Technique
2 minutes massage into the scalp. To enhance the absorption, a wrap was subsequently applied to the scalp. This step was intended to create a warm, occlusive environment that could improve the penetration of active ingredients into the skin and hair follicles.
When Natural Extracts Aren’t Enough: Why Hair Transplantation Remains the Most Reliable Solution
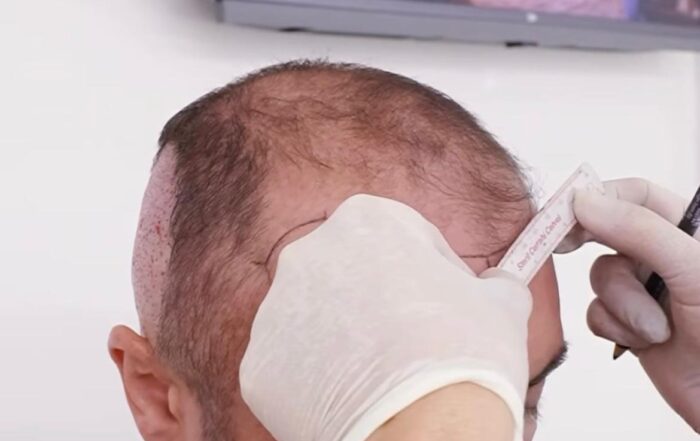
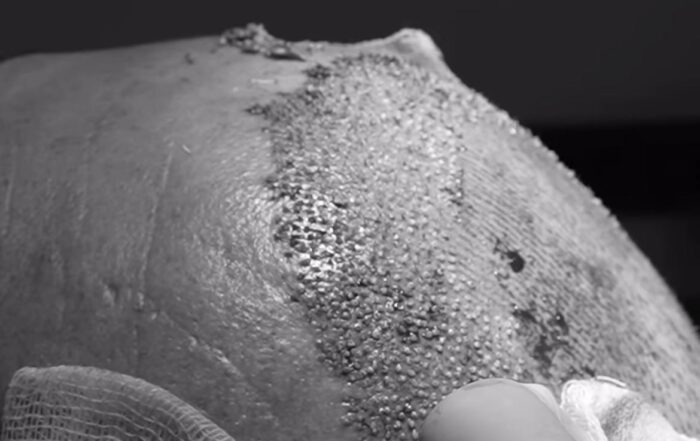
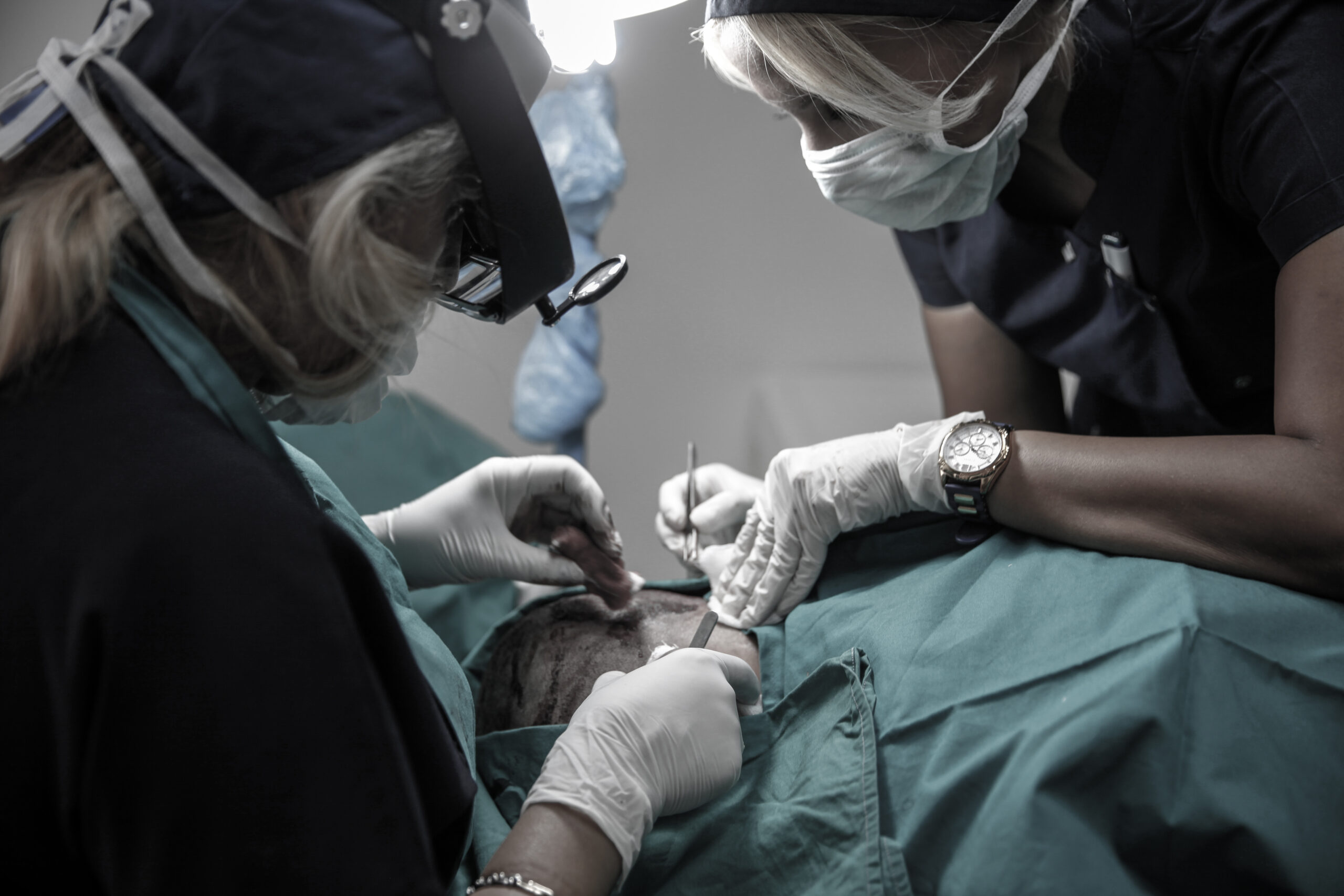
While rosemary oil and other natural treatments may offer moderate improvement in hair density and scalp health, they often require consistent, long-term use and may not be effective for all individuals—especially those with advanced hair loss. For patients seeking a permanent and visibly fuller result, hair transplantation offers the most predictable and lasting outcome. Performed by a qualified hair restoration surgeon, modern transplant techniques such as FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) deliver natural-looking results with minimal downtime and long-term success.
References
- Bin Rubaian NF, Alzamami HFA, Amir BA. An Overview of Commonly Used Natural Alternatives for the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia, with Special Emphasis on Rosemary Oil. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024;17:2495-2503. Published 2024 Nov 5. doi:10.2147/CCID.S470989
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, Sahebkar A. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015;13(1):15-21.
- ÖZMEN, İ., ÇALIŞKAN, E., ARCA, E., AÇIKGÖZ, G., & KOÇ, E. (2015). Efficacy of aromatherapy in the treatment of localized alopecia areata: A double-blind placebo controlled study. Gulhane Medical Journal, 57(3), 233-236. https://doi.org/10.5455/gulhane.38258
References
- Bin Rubaian NF, Alzamami HFA, Amir BA. An Overview of Commonly Used Natural Alternatives for the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia, with Special Emphasis on Rosemary Oil. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024;17:2495-2503. Published 2024 Nov 5. doi:10.2147/CCID.S470989
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, Sahebkar A. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015;13(1):15-21.
- ÖZMEN, İ., ÇALIŞKAN, E., ARCA, E., AÇIKGÖZ, G., & KOÇ, E. (2015). Efficacy of aromatherapy in the treatment of localized alopecia areata: A double-blind placebo controlled study. Gulhane Medical Journal, 57(3), 233-236. https://doi.org/10.5455/gulhane.38258